The Harmonic Journey: Unveiling the Evolution and Varieties of Accordions
TL;DR: The accordion has evolved from an early 19th-century instrument into a globally revered music…….

TL;DR: The accordion has evolved from an early 19th-century instrument into a globally revered musical staple, with significant innovations like Friedrich Buschmann's free-reed system of 1829 and subsequent advancements such as chromatic buttons and the Stradella bass system. These improvements enhanced the accordion's sound quality, dynamic range, and user-friendliness, enabling it to cross genres and become more accessible through mass production. Modern technology has further enriched its sound with digital components, allowing contemporary musicians to push the boundaries of what the instrument can do. The accordion's journey from its origins to today showcases human creativity and the impact of music technology.
Accordions are intricate instruments with reed organs, keyboard configurations, and bellows mechanisms. They operate through airflow from the bellows, activating two sets of reeds for expansion and contraction, fine-tuned to produce specific pitches as musicians press buttons on the keyboard. The bellows, made from materials like leather or synthetic fabric, can be configured in dual or tripartite sections, with a chesnut or paladini regulating airflow to the reeds. Accordions are multifaceted, with variations like piano accordions, button accordions (including diatonic and chromatic types), and the specialized bandoneon, each offering distinct tonalities and capabilities suitable for classical, folk, jazz, and pop music styles. The button accordion, originating from Germany, is particularly notable for its versatility and user-friendly design, gaining prominence in genres such as Irish traditional music and classical compositions worldwide. Its portability, rich tonal range, and adaptability make it a preferred choice for musicians exploring a wide repertoire of accordion music.
discover the fascinating world of accordions, an instrument whose rich history and diverse applications span across various musical genres. This article delves into the evolution of the accordion from its inception to its modern-day role as a versatile musical expression. We’ll explore the intricate components that make up this unique instrument, the different types of accordions catering to every musician’s needs, and their cultural significance across continents. From Europe’s enduring romance with the accordion to its vibrant roles in Latin music traditions like Zydeco, understand how these hand-held masterpieces have shaped global soundscapes.
We’ll guide beginners through the basics of learning to play and uncover advanced techniques for seasoned players. Maintenance and repair tips will ensure your accordion remains a reliable companion on your musical journey. Iconic accordionists who’ve left an indelible mark on music history, such as Nino Rota, Terry Huval, and Astor Piazzolla, will be highlighted for their contributions. Moreover, we’ll examine the accordion’s role in a myriad of musical genres, from classical to rock, and how modern designs and technology have propelled it into the future. Accordion enthusiasts can look forward to insights into the global scene, including major events, local communities, and museums dedicated to this captivating instrument. Join us as we celebrate the accordion’s legacy and its enduring presence in the world of music.
- The Evolution of Accordions: From Invention to Modern Expression
- Key Components of an Accordion: Understanding the Mechanics
- Types of Accordions: A Diverse Range for Every Musician
- – Button Accordions
The Evolution of Accordions: From Invention to Modern Expression

The accordion, an instrument that has captivated listeners with its rich harmonic textures and melodic versatility since its inception, has undergone a remarkable evolution over the centuries. Originating in the early 19th century, the first prototypes were cumbersome and rudimentary, yet they laid the groundwork for what would become a beloved musical staple around the globe. The invention of the free-reed system by Friedrich Buschmann in 1829 was a pivotal moment in the accordion’s development, allowing for more nuanced tone production and a broader dynamic range. As the instrument matured, it became smaller, more durable, and easier to play, with key innovations such as the development of chromatic buttons by System Böhm and the introduction of the Stradella bass system enhancing its expressive capabilities.
The 20th century saw the accordion transcend traditional folk and dance music genres, influencing jazz, classical, and even rock. The instrument’s portability and the breadth of sounds it could produce made it an attractive choice for artists seeking a unique sound. Advancements in manufacturing techniques led to the production of high-quality mass-market accordions that were both affordable and accessible. Today, the accordion continues to evolve with technological advancements, incorporating digital components that expand its tonal possibilities. Accordionists now push the boundaries of musical expression, exploring new genres, and redefining the potential of this remarkable instrument. From its humble beginnings to its modern-day incarnations, the accordion remains a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring power of music.
Key Components of an Accordion: Understanding the Mechanics

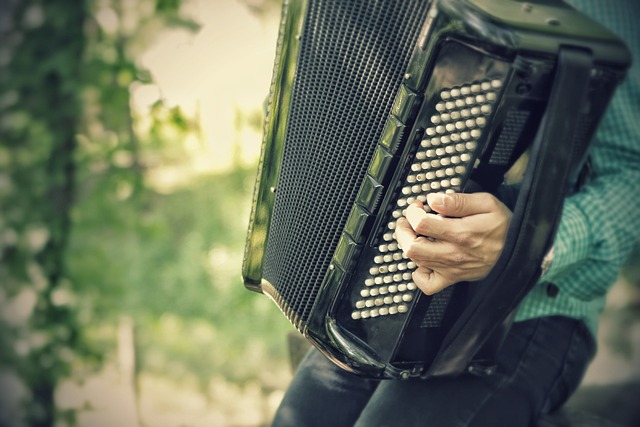
Accordions are intricate musical instruments characterized by their reed organs, keyboard layouts, and bellows systems. The heart of an accordion lies in its reeds, which produce sound when air from the bellows is directed through them. There are two sets of reeds in an accordion: one set for the notes played when the bellows expands, and another for when the bellows contracts. These reeds are tuned to specific pitches and are categorized as either chords or melody reeds. The keyboard, or ‘manual,’ of an accordion is where the musician presses buttons to engage these reeds. It’s designed with two or three rows of keys, each row corresponding to a different set of notes or chords that can be played in combination.
The bellows, the lungs of the instrument, are constructed from durable materials like leather or synthetic fabrics. They come in various sizes and are pivotal in determining the volume and tonal range of the accordion. The bellows can be split into two or three sections, enabling musicians to play different registers without changing their hand position on the keyboard. The mechanism that connects the bellows to the reeds is known as the ‘bellows chesnut’ or ‘paladini,’ which ensures airflow from the bellows to the reeds in a controlled manner. Understanding these components and how they function together is essential for mastering the accordion, as it allows players to produce a wide array of sounds and music styles, from classical to folk, jazz to pop.
Types of Accordions: A Diverse Range for Every Musician

Accordions are a family of bellows-driven musical instruments, each offering a unique set of tones and functionalities that cater to diverse musical styles and preferences. The world of accordions is rich with variety, from the compact and versatile piano accordion to the larger and more robust bandoneon, each type designed to meet the needs of different musicians and genres. Piano accordions, with their keyboard rows and bass buttons, provide a pianistic touch and are widely used in classical and contemporary music. They come in different sizes, from small one-row models suitable for beginners to expansive four-row instruments capable of producing complex harmonies. On the other hand, button accordions, such as the diatonic and chromatic varieties, are staples in folk and traditional music scenes. These instruments offer a range of buttons that allow players to produce chords, melodies, and even bass lines, making them highly adaptable for both solo performances and ensemble playing.
For those interested in the rich soundscapes of Latin American music, the bandoneon is an essential instrument. Originating from Germany and becoming iconic in Argentine tango and other South American genres, the bandoneon’s complex array of treble and bass buttons allows for intricate melodies and counterpoints that are deeply expressive. Similarly, the melodeon, with its gentle reed sounds, is a favorite for Celtic and folk musicians. It often features a smaller bellows and fewer keys compared to other types of accordions, which contributes to its mellow and distinctive tone. Regardless of the type, every accordionist can find an instrument that suits their style, whether they are playing classical pieces, jazz standards, or traditional folk tunes. The versatility and richness of accordions make them a treasured instrument in various musical traditions around the globe.
– Button Accordions

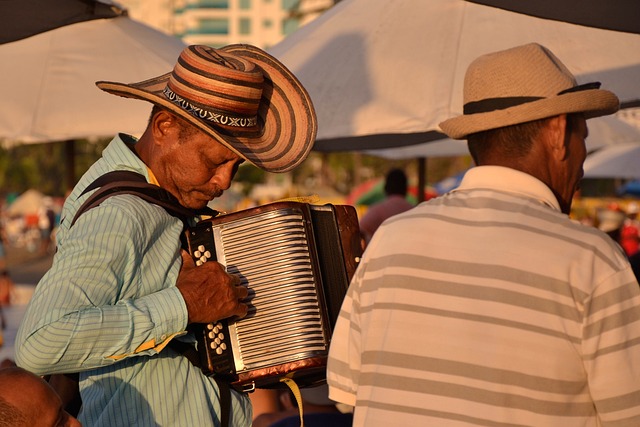
Accordions are a versatile and beloved musical instrument, with the button accordion being one of its most popular varieties among musicians across the globe. The button accordion stands out due to its user-friendly key arrangement, which allows for quicker finger work and transitions between chords compared to the traditional piano or chromatic accordions. This particular type of accordion has a rich history, tracing back to the early 19th century in Germany, where it was developed from earlier free-bass systems into the more familiar button layout that we see today. The instrument’s design facilitates a wide range of tones and melodies, making it a staple in various musical genres, from folk and traditional to contemporary and even classical music arrangements.
Button accordions typically feature two or three rows of buttons on the treble side and one or two rows on the bass side for the melody and harmony, respectively. The treble system can be played with both hands, with the right hand playing the melody and rhythm, while the left hand accompanies by playing the chords. This layout has made the button accordion a favorite in many cultures, particularly in Ireland, where it’s synonymous with traditional music, and in countries like Scotland, France, and Italy, where it’s equally revered. The instrument’s compact size allows for easy transportation and performance, making it an ideal choice for both professional musicians and enthusiasts who wish to explore the expansive world of accordion music.