Optimizing Weight Distribution: The Key to Perfect Crepes with Crepe Pans
TL;DR:Weight distribution in crepe pans is critical for even cooking and browning of thin pastries l…….

TL;DR:
Weight distribution in crepe pans is critical for even cooking and browning of thin pastries like crepes and pancakes. Key factors influencing this include pan material (copper, aluminum, cast iron), design (flat-bottomed), thickness, shape, size, and coating. Copper and aluminum conduct heat uniformly, while cast iron maintains consistent heat. Preheating, regular flipping, and temperature control with butter or oil ensure even heat application. Metal crepe pans enhance heat conductivity for consistent results, and practice improves cooking technique for delightful crepes every time.
“Unleash your inner chef with a deeper understanding of weight distribution in cookware, especially when crafting perfect crepes. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals, highlighting how even weight distribution ensures consistent cooking. We explore the unique role of crepe pans in promoting uniform heat transfer for golden-brown, fluffy crepes.
From pan materials to cooking techniques, discover factors influencing weight distribution and learn expert tips to optimize your crepe-making experience. Master the art with our insights on using crepe pans for consistent results.”
- Understanding Weight Distribution: The Basics
- Crepe Pans and Their Role in Even Cooking
- Factors Affecting Weight Distribution in Cookware
- Tips for Optimizing Weight Distribution for Perfect Crepes
Understanding Weight Distribution: The Basics

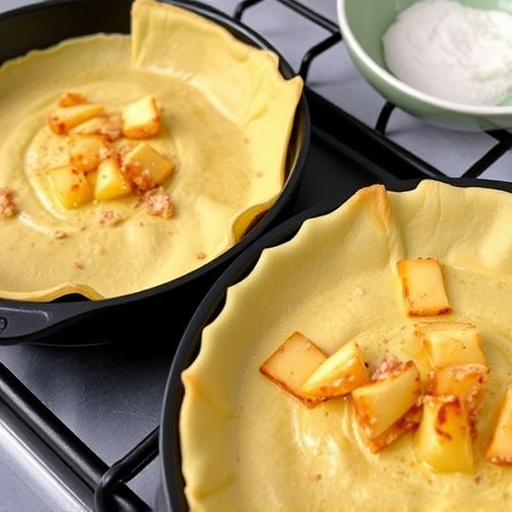
Weight distribution is a fundamental concept in cooking, especially when using specialized equipment like crepe pans. It refers to how heat and weight are evenly or unevenly dispersed across the cooking surface. This process significantly impacts the outcome of food preparation, particularly in terms of even cooking and browning. Crepe pans, known for their thin, round shape and non-stick coating, demand precise weight distribution to ensure a delicate and consistent bake.
When a crepe pan is used, the heat from the source (stove or electric heating element) needs to be evenly transferred to the entire cooking surface to prevent hot spots. Hot spots can lead to uneven cooking, with certain areas burning while others remain undercooked. Proper weight distribution ensures that the pan retains heat consistently, facilitating even heat transfer and browning of food items placed on it. This is crucial for achieving desirable culinary results when preparing crepes, pancakes, or other thin pastries.
Crepe Pans and Their Role in Even Cooking

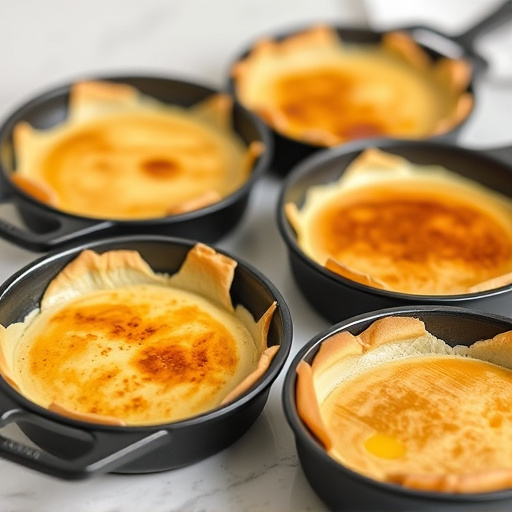
Crepe pans play a pivotal role in achieving even cooking, especially for delicate and thin pancakes or crepes. These specialized cookware pieces are designed with a flat, smooth surface and often feature a non-stick coating to ensure that your batter spreads evenly and doesn’t stick. The uniform heat distribution across the pan’s surface is key to creating perfectly cooked crepes—the batter should flow smoothly, forming a thin layer that cooks equally on both sides.
Compared to standard frying pans, which might have hot spots or uneven heating, crepe pans are crafted to eliminate such issues. Their shape and design allow for precise temperature control, resulting in a golden-brown exterior and a tender interior. This even cooking ensures that your crepes rise evenly, cook thoroughly, and maintain their texture, making them the ideal choice for both novice and expert cooks looking to master the art of crepe making.
Factors Affecting Weight Distribution in Cookware

Weight distribution in cookware, like crepe pans, is influenced by several key factors. One major factor is the material used; different metals conduct heat differently. For instance, copper and aluminum excel at evenly distributing heat due to their excellent thermal conductivity, whereas cast iron can hold heat more consistently across its surface. The design of the pan also plays a crucial role—flat-bottomed pans ensure uniform contact with a cooking surface, promoting equal heat distribution. Additionally, the thickness of the cookware matters; thinner pans heat up faster but may have hot spots, while thicker ones offer more even heating but take longer to reach optimal temperatures.
The shape and size of crepe pans are also significant. Smaller pans facilitate quicker heating and better control during cooking, ideal for delicate crepes. Larger models, however, provide more space for larger batches or dishes that require a wider cooking surface. Lastly, the coating on the pan’s interior impacts weight distribution; non-stick coatings can cause hot spots due to their non-conductive nature, while smooth, uncoated metal ensures better heat transfer and even cooking.
Tips for Optimizing Weight Distribution for Perfect Crepes

To achieve perfect crepes, optimizing weight distribution is key. When using crepe pans, ensure even heat application by distributing the weight evenly across the surface. This can be done by regularly checking and flipping the crepe to prevent hot spots from forming, which could cause uneven cooking. A good practice is to preheat your pan for a few minutes before pouring in the batter; this helps create a stable temperature base.
Additionally, consider the material of your crepe pans. Metal pans tend to conduct heat more efficiently than non-stick varieties, ensuring consistent weight distribution. Adjusting the amount of butter or oil used can also help manage heat retention and release, promoting even cooking. Remember, practice makes perfect; with time, you’ll master the art of distributing weight optimally for consistently delightful crepes.
In conclusion, achieving perfect crepes begins with understanding and optimizing weight distribution. Crepe pans play a pivotal role in ensuring even cooking by promoting uniform heat transfer. By considering factors like pan material, surface texture, and design, you can enhance weight distribution, resulting in consistently cooked crepes. Implement the tips outlined in this article to master the art of weight distribution and elevate your crepe-making skills using specialized crepe pans.