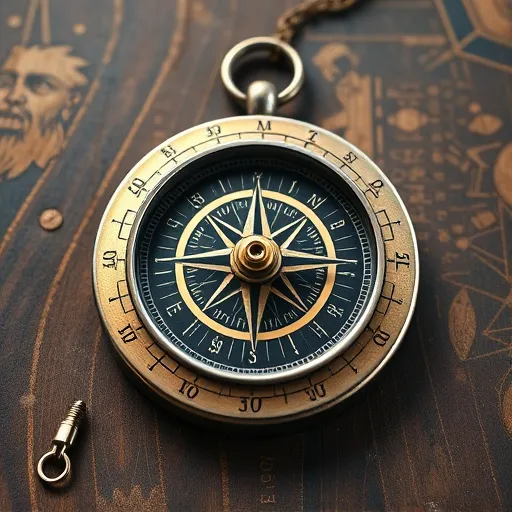
Mastering Land Navigation with Lensatic Compasses: A Comprehensive Guide
Lensatic compasses are superior navigation tools compared to traditional magnetic compasses, offeri…….
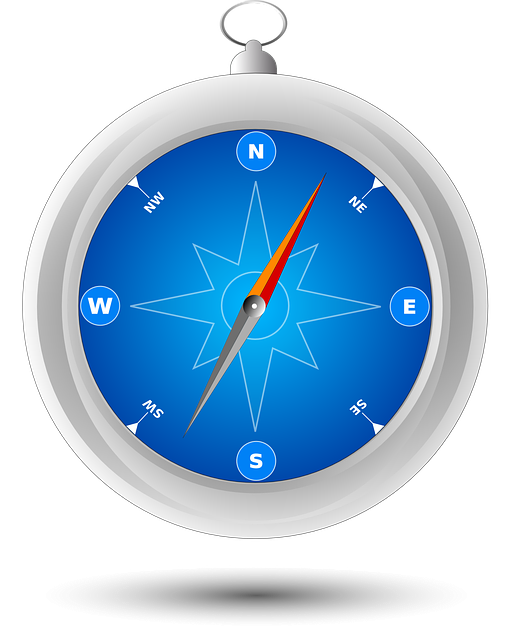

Lensatic compasses are superior navigation tools compared to traditional magnetic compasses, offering clearer and more accurate land navigation through their lensatic design, which includes a transparent reticle and an overlying lens for precise alignment with map grid lines or natural features. These compasses are crucial for differentiating between magnetic north, true north, and grid north, and come with adjustable settings to correct for magnetic declination, making them indispensable for explorers in areas without reliable GPS signals. Their protective lenses enhance visibility under various lighting conditions, while the full 360-degree scale, rotating repeater needle, and sighting lid with target mark allow for accurate bearings even in low-light or when celestial cues are not available. The liquid-filled vial ensures stability, and the base plate includes a ruler and protractor for pacing and angle measurements, making lensatic compasses essential tools for precise land navigation across diverse terrains. Regular cleaning, maintenance, and calibration are necessary to maintain their accuracy and reliability as a magnetic tool for orientation in various landscapes.
When venturing into the wilderness, a reliable navigation tool is indispensable. This article delves into the mastery of land navigation using lensatic compasses, a pivotal instrument for explorers and survivalists alike. We will unravel their mechanics, explore their functionality, and guide you through the nuances of taking accurate bearings. Whether you’re an avid hiker or a seasoned navigator, understanding how to select and maintain your lensatic compass for optimal performance across diverse terrains is crucial. Join us as we shed light on the compass and its role as a cornerstone in the realm of land navigation.
- Understanding Lensatic Compasses: The Cornerstone of Land Navigation
- The Mechanics and Functionality of Lensatic Compasses
- Mastering the Art of Taking Bearings with a Lensatic Compass
- Selecting and Maintaining Your Lensatic Compass for Optimal Performance in Various Terrains
Understanding Lensatic Compasses: The Cornerstone of Land Navigation

Lensatic compasses are indispensable tools for land navigators, offering a reliable method to determine direction with precision. Unlike traditional magnetic compasses, lensatic models incorporate a transparent reticle over the compass dial and a lens above it. This design allows users to superimpose a rotating index onto the map’s grid lines or terrain features, facilitating quick and accurate navigation readings. The instrument’s clarity is enhanced by the lens, which also aids in aligning the compass with natural landmarks during daylight hours or stars at night.
Navigators must be adept at interpreting the compass’s readings, which involve understanding the relationship between the magnetic north, true north, and the grid north on a map. The lensatic compass provides a simple yet effective way to account for magnetic declination, the angle between magnetic north and true geographic north. By adjusting the compass’s reverted settings, one can compensate for this difference, ensuring that bearings taken are directed towards the intended destination rather than an erroneous point. Mastery of these instruments is crucial for any explorer venturing into areas where GPS signals may be unreliable or unavailable, making lensatic compasses a cornerstone skill in the field of land navigation.
The Mechanics and Functionality of Lensatic Compasses

Lensatic compasses are a cornerstone in the realm of land navigation for outdoor enthusiasts and military personnel alike. Unlike traditional magnetic compasses, lensatic models incorporate a series of lenses above the compass dial, which not only protect the compass mechanism but also provide an amplified image of the floating needle for clearer reading under various lighting conditions. The compass card, or dial, is marked with lines that correspond to the 360-degree scale of the Earth’s surface and includes a rotating replica of the magnetic compass needle, known as the “repeater needle,” which aligns with a fixed cursor located at the top of the compass. The user adjusts the compass for magnetic declination, the angle between true north and magnetic north, to ensure accurate readings. The lensatic compass also features a sighting lid with an etched target mark, allowing users to aim the compass directly at an object or feature, such as a hilltop or a distinctive tree, to take a bearing. This method of sighting down the etched line through the lenses and onto the desired point enables users to navigate with precision even in low-light conditions or during the day when the sun’s position makes a traditional sighting difficult.
The functionality of lensatic compasses is rooted in their ability to accurately measure angles, both horizontally and vertically, which is essential for tasks like determining one’s orientation relative to the Earth’s magnetic field or calculating the distance between points when used in conjunction with pacing or map measurement techniques. The lenses magnify the compass needle, which is suspended over a filled glass vial that contains a liquid providing damping to minimize the effects of shocks and vibrations. This design allows for stable readings even when the user is moving. The compass’s base plate also features a ruler for pacing and a protractor scale for taking precise angle measurements, making it a versatile tool for various land navigation tasks. Users must be adept at interpreting the compass reading to determine cardinal directions and convert them into grid coordinates on a map, ensuring effective navigation in environments where GPS signals may not be reliable or available.
Mastering the Art of Taking Bearings with a Lensatic Compass

When it comes to land navigation, mastering the art of taking bearings with a lensatic compass is an indispensable skill for anyone venturing into unfamiliar terrain. A lensatic compass, such as the traditional L1A or L3A models, offers a precise and reliable method for navigation when other tools like GPS may not be available or reliable. To begin, one must understand the fundamental differences between a lensatic compass and a magnetic compass. Unlike its simpler counterpart, the lensatic compass features a movable dial and a series of lenses that allow for precise alignment with a map’s grid north and the actual geographic north.
The process of taking bearings starts with properly setting up the compass. Firstly, align the direction of travel arrow with your intended path on the map. Then, use the built-in index mirrors or separate clinometer to reflect a light source so that the compass’s rotating red and black sectors come into precise alignment with the grid north line on the map. This alignment is crucial as it ensures that the compass needle, which follows the earth’s magnetic field, can be read accurately in relation to true north. Once aligned, you can take a reading by noting the position of the red or black end of the sectors pointing towards your starting point on the map. This reading will give you the bearing to follow, which you can then use to navigate your route across the landscape with confidence. Practice and familiarity with the lensatic compass are key to developing proficiency in its use. Whether you’re an avid hiker, a survivalist, or part of an expedition team, learning to take accurate bearings with a lensatic compass is a vital skill that complements any navigation toolkit.
Selecting and Maintaining Your Lensatic Compass for Optimal Performance in Various Terrains

When venturing into diverse terrains for land navigation, selecting and maintaining a Lensatic compass is paramount for optimal performance. A Lensatic compass, particularly a magnetic compass, is an indispensable tool for anyone who relies on traditional methods of orientation in the field. It’s crucial to choose a model that suits your specific needs; consider factors such as durability, ease of use, and the clarity of its lens and degree markings. For example, if you frequently encounter wet environments, a waterproof compass would be more suitable than one that is prone to moisture damage.
Once you have your Lensatic compass, regular maintenance is key to ensuring it remains accurate and reliable. Clean the instrument with a soft, lint-free cloth after each use to remove any grit or residue that could interfere with its functioning. Check the liquid inside the compass capsule; if it’s cloudy or leaking, it should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Calibrate your compass periodically by comparing its readings with known directions, such as true north indicated by a compass app on your smartphone or a map. This ensures that the magnetic needle is aligned correctly and compensates for local magnetism, which can skew your readings. By taking these steps to select and maintain your Lensatic compass, you’ll have a dependable ally in navigation across various terrains, from the dense forests to the arid deserts.