Global Trade Evolution: Weaving’s Technological and Sustainable Future
The global weaving sector has undergone a transformative journey from an artisanal practice to a sop…….

The global weaving sector has undergone a transformative journey from an artisanal practice to a sophisticated, technology-driven industry integral to international trade. Historically, the spread of weaving techniques was fueled by cultural exchange and the establishment of trade routes, which led to significant advancements, including the Industrial Revolution's introduction of mechanical looms that drastically increased production. Today, cutting-edge technologies in weaving emphasize precision, innovation, and a global supply chain that combines traditional craftsmanship with advanced manufacturing processes. Key players like China, India, and Turkey, alongside nations like Italy and Germany, dominate the industry by leveraging their unique resources and adaptability to cater to diverse global markets. Recent advancements have further revolutionized weaving, with automated looms guided by sophisticated software enabling the production of complex textiles quickly and efficiently. These technologies also include computerized design systems and IoT integration for real-time monitoring and adjustments, enhancing quality and reducing waste. Sustainability and ethical considerations are increasingly at the forefront, as the industry adopts eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient technologies, and humane labor practices to align with a market that values both ecological integrity and weaver welfare. The convergence of innovation, sustainability, and responsiveness positions the global weaving sector at the forefront of economic growth within the trade landscape, poised to meet the evolving needs of consumers worldwide.
Global trade has always been a rich tapestry, with weaving as one of its foundational threads. This article delves into the intricate patterns woven through history by the weaving industry, tracing its evolution within international commerce. From the craft’s ancient roots to modern production techniques, we explore how key players and distinct regions have shaped this industry. Technological innovations are transforming the art of weaving, leading to new possibilities. Moreover, sustainable practices and ethical considerations have become integral to the weaving sector, highlighting a shift towards responsible manufacturing. As we examine current trends and predict future developments, it’s clear that weaving remains a dynamic field with endless opportunities for growth and innovation in global trade.
- The Evolution of Weaving in Global Trade
- Key Players and Regions Shaping the Weaving Industry
- Technological Innovations Revolutionizing the Art of Weaving
- Sustainable Practices and Ethical Considerations in Modern Weaving
- The Future of Weaving: Trends, Predictions, and Opportunities
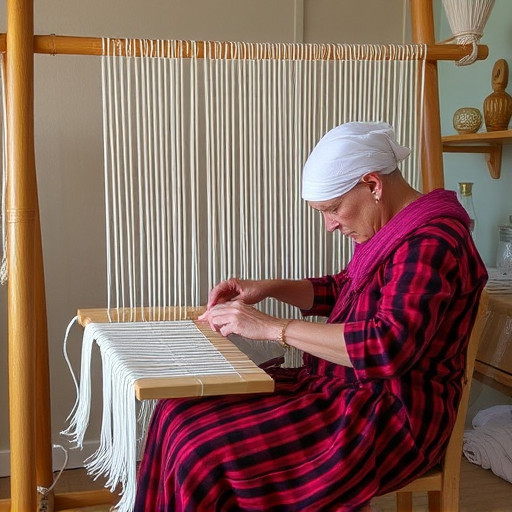
The Evolution of Weaving in Global Trade

Over the centuries, weaving has undergone a remarkable transformation from a simple craft to a complex component of global trade. Initially, weaving was a localized activity, with each region developing its unique techniques and patterns. As civilizations expanded and intercontinental trade routes were established, the exchange of textile technologies and woven goods became a vehicle for cultural diffusion. The Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal point in the evolution of weaving, as mechanical looms greatly increased production capacity and efficiency. This shift enabled manufacturers to meet the growing global demand for textiles, leading to the rise of textile industries in various countries.
In contemporary times, advancements in technology continue to shape the landscape of weaving within global trade. With the advent of digitalization and automation, precision and innovation have become cornerstones of the industry. Today, weaving is a highly integrated process that spans across borders, with raw materials sourced from different regions and finished products distributed worldwide. The global supply chain has made it possible for weaving artisans to collaborate across distances, blending traditional techniques with modern technology to create textiles that cater to diverse markets. This symbiosis of tradition and innovation not only fuels economic growth but also celebrates the cultural heritage that is woven into each thread of global trade.
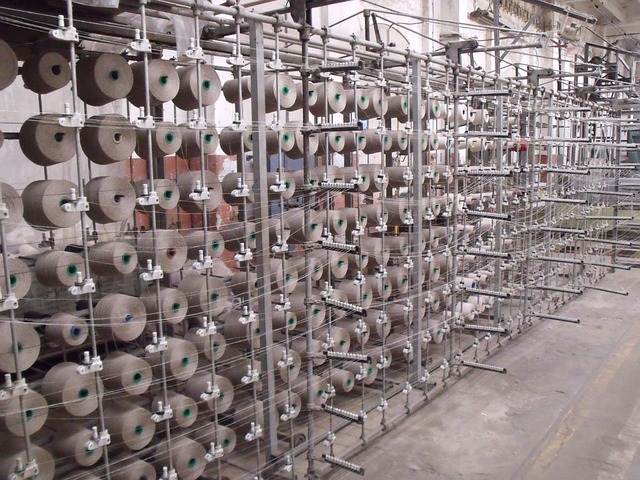
Key Players and Regions Shaping the Weaving Industry

The global weaving industry is a complex tapestry woven by diverse key players, each contributing to its intricate pattern. Major manufacturers across countries like China, India, and Turkey dominate the landscape, leveraging their advanced technology, skilled labor force, and strategic market positions. These nations are not only pivotal in raw material production but also excel in sophisticated weaving techniques that cater to a wide array of markets, from luxury fashion to industrial applications. In Asia, for instance, China stands out as a leader in synthetic fibers weaving, while India’s expertise lies in the traditional handloom sector. The competitive edge of these regions is further enhanced by their ability to adapt to global trends and consumer demands, ensuring their continued dominance in the international market. Meanwhile, countries such as Italy and Germany are influential due to their high-end machinery manufacturing, which significantly shapes the technological advancements within the industry. These regional dynamics contribute to a vibrant and dynamic global weaving industry that is both innovative and responsive to economic shifts and consumer needs.
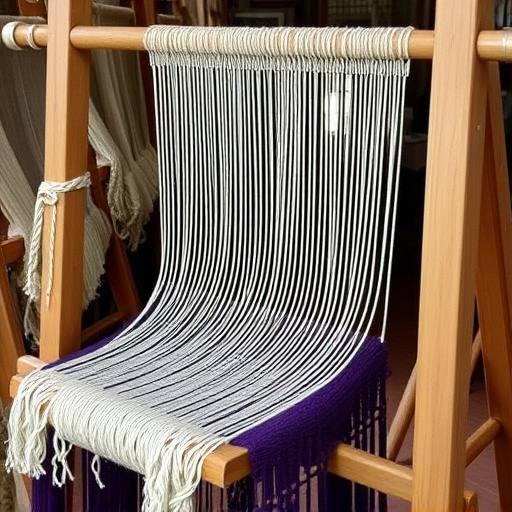
Technological Innovations Revolutionizing the Art of Weaving

The art of weaving, an age-old craft that has evolved over millennia, has undergone a seismic transformation in recent times due to groundbreaking technological innovations. These advancements have not only improved the efficiency and precision of traditional weaving techniques but have also expanded the possibilities for designers and manufacturers around the world. Automated looms, powered by sophisticated software algorithms, are now capable of producing complex patterns with unprecedented consistency and speed. This automation has enabled weavers to experiment with a wider array of materials, from high-performance polymers to environmentally sustainable fibers, leading to the creation of textiles that are both innovative and eco-friendly.
In addition to these mechanical leaps, digital technology has introduced new dimensions to the weaving process through computerized design systems and 3D modeling software. These tools allow designers to visualize and simulate textile structures before they are physically woven, optimizing the design for both aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Furthermore, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into weaving machinery facilitates real-time monitoring and adjustments during production, ensuring high-quality outcomes and minimizing waste. The confluence of these technologies not only revolutionizes the traditional practice of weaving but also positions it at the forefront of the global trade landscape, where innovation continues to drive progress in this dynamic field.
Sustainable Practices and Ethical Considerations in Modern Weaving

The interplay between sustainable practices and ethical considerations is a critical aspect in the realm of modern weaving, an integral component of global trade. Artisans and industries alike are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly methods to minimize their ecological footprint. The use of organic and locally sourced materials has become more prevalent, reducing the reliance on synthetic fibers that can be detrimental to both human health and the planet. These sustainable practices extend to water conservation in dyeing processes and energy-efficient machinery in large-scale production facilities. Moreover, ethical considerations are at the forefront as consumers demand transparency and fair labor practices within supply chains. Ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions for weavers is not only a moral imperative but also a way to foster long-term, sustainable economic growth in communities that depend on the weaving craft. The integration of these ethical and sustainable principles is not only beneficial for the environment and society but also serves as a competitive advantage in the global marketplace, appealing to an increasingly conscientious consumer base that values both the integrity of the product and the well-being of its creators.
The Future of Weaving: Trends, Predictions, and Opportunities

The future of weaving within the global trade landscape is an intricate tapestry that intertwines with technological advancements, sustainable practices, and evolving consumer demands. As automation and digitalization continue to reshape manufacturing processes, the weaving sector is adapting to incorporate these innovations. Smart looms and advanced materials are paving the way for a new generation of textiles with enhanced properties, catering to industries beyond traditional clothing and home goods. The rise of wearable technology, for instance, has created a niche market for fabrics that can integrate electronics seamlessly, opening up opportunities in healthcare monitoring, fitness tracking, and personal security.
Sustainability is another key driver shaping the future of weaving. There is a growing emphasis on eco-friendly production methods, waste reduction, and the use of recycled materials. This shift is not only a response to environmental concerns but also reflects a consumer base that is increasingly conscious of the ecological impact of their purchases. The demand for ethically produced, high-quality textiles presents a significant opportunity for weaving businesses that can effectively integrate sustainable practices without compromising on quality or innovation. As global trade patterns evolve, the ability to pivot quickly and respond to these trends will be crucial for companies in the weaving industry to thrive in the coming years.